
Refractory heat-up using heating coils is a crucial process in industries such as oil and gas, metallurgy, and ceramics. Refractories, which are heat-resistant materials lining furnaces, kilns, and reactors, must be properly heated to achieve optimal performance and durability. Heating coils, often made from materials like nichrome or Kanthal, are used to gradually and uniformly raise the temperature of the refractory lining.
The process begins by installing heating coils within the refractory structure. These coils generate heat when an electric current passes through them. The heat-up process is carefully controlled to avoid thermal shock, which can cause cracking or damage to the refractory material. Typically, the temperature is increased in stages, with controlled holding periods to ensure even heating and to allow any moisture trapped within the refractory to evaporate safely.
Using heating coils for refractory heat-up ensures that the lining achieves the necessary temperature and physical properties for effective operation. This method promotes longer refractory life, improved efficiency, and reduced downtime for maintenance in high-temperature industrial applications.
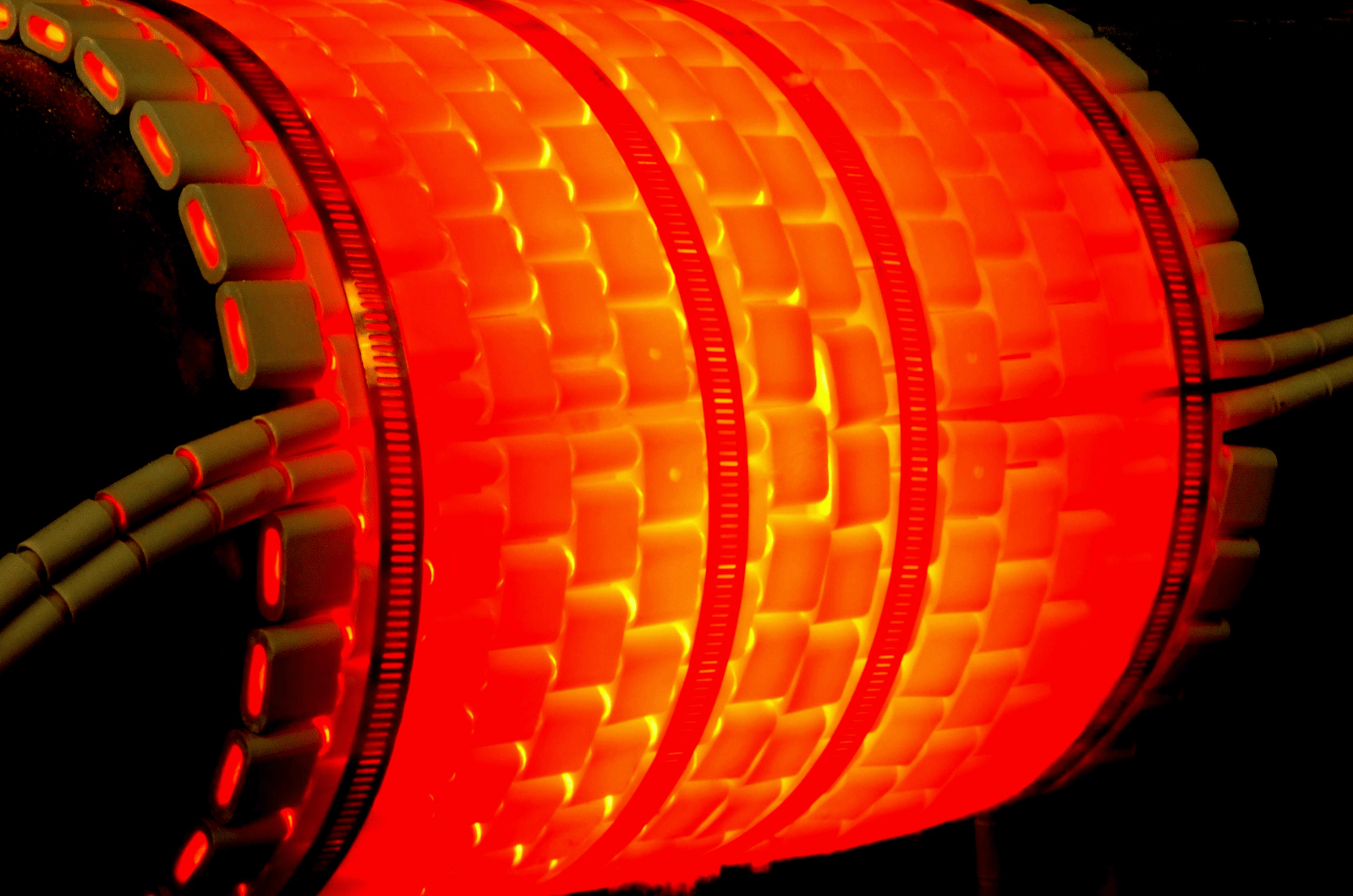
Using heating coils for refractory heat-up ensures uniform temperature distribution, reduces thermal stress, extends refractory life, and enhances overall operational efficiency in industrial heating applications.

